low end tidal co2 after intubation
Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after. Can the value of end tidal CO2 prognosticate ROSC in patients coding into emergency department with an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords.

. For example increased dead space is seen in pulmonary embolism in pneumonia or. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as. Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector End tidal CO2 detector Secondary signs.
In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. The normal values of end-tidal CO 2 is around 5 or 35-37 mm Hg. Alveolar dead space may be increased in most types of lung disease reflecting dysfunction at the alveolar vascular or airway level.
Consequently a strategy of high-frequency low-tidal volume breaths will tend to achieve less CO2 clearance for any specific total minute ventilation. This disposable bedside detector registers three ranges of CO2 concentration. BMC Anesthesiol 13 20 2013.
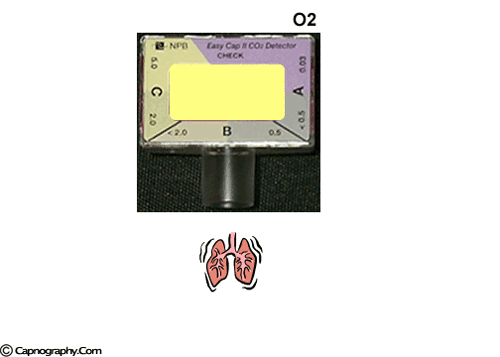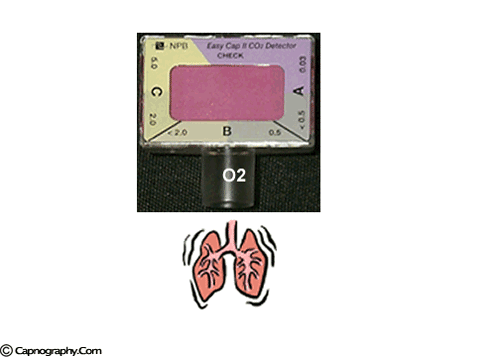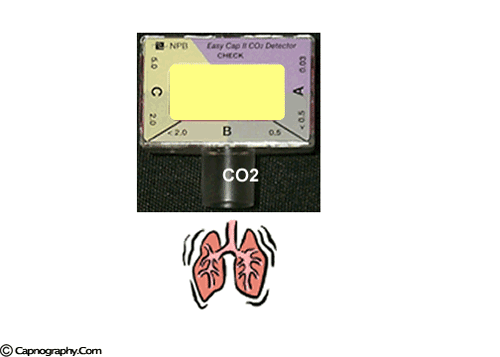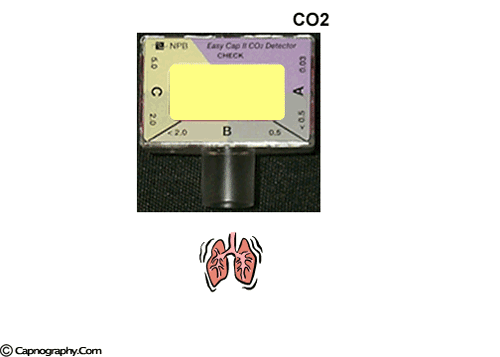
B beige indicates moderate levels and probable tracheal intubation. CO2 EtCO2 the maximum CO2 concentration at the end of each tidal breath can be used to assess disease severity and response to treatment. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle.
Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2. A semiquantitative colorimetric FEF end-tidal CO2 detector Fenem Inc New York NY was used to evaluate endotracheal versus esophageal intubation. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg.
End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is a more objective method812 and is recommended as the best method to confirm correct ETT placement by the 2015 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation13 In a study of 100 intubation episodes 39 of 40 oesophageal intubations were correctly identified by ETCO 2 monitoring using capnography. End-tidal carbon dioxide and defibrillation success in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Misting increased SaO2 Types of End-Tidal CO2 Qualitative Yes or No.
2 See Figure. The patients physical examination vital. Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. In emergently ventilated trauma patients low end-tidal CO 2 and low cardiac output are associated and correlate with hemodynamic instability hemorrhage abnormal pupils and death.
End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status. End-tidal carbon dioxide reflects CO 2 concentration of alveoli emptying last. We present a case in which the Dräger Primus Dräger Medical AGCo KG Lüberck Germany anesthesia monitor displayed false readings of low end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 immediately after intubation.
Savastano S et al. A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function.
An end-tidal capnography waveform is a simple graphic measurement of how much CO 2 a person is exhaling. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO.

Monitoring Ventilation With Capnography Nejm
Emergency Intubations Capnography

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

3 Things To Know About Capnography And Advanced Airways Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Evidence Supports Using End Tidal Carbon Dioxide To Detect Prehospital Sepsis Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

How To Read And Interpret Capnography Waveforms Infinium Medical

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Capnography Abnormal Waveforms Respiratory Care Respiratory Therapy Respiratory Therapist

What S In A Wave Form Utilizing End Tidal Capnography For More Than Intubation Confirmation Criticalcarenow

Pv Card Continuous End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In Cardiac Arrest Cardiac Nursing Cardiac Arrest Medical Knowledge

